Simple introduction, Symptoms, Treatments and Prevention methods of scabies
What is scabies?
Scabies is a contagious parasitic disease caused by a tiny mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. This insect burrows into your skin, lives there producing eggs, and more and more mites, causing intense itching and a rash. This is a troublesome and psychologically distressing condition that affects the day-to-day life of the affected individual.
Prevalence is high in tropical countries, while crowded conditions like prisons, orphanages and boarding schools facilitate the parasitic transmission. The WHO has classified it as a neglected tropical disease, even though 200 million people are affected worldwide. Children and older people in resource-poor areas are at a greater risk of scabies. It spreads by direct skin contact, human to human, but not through other animals.
The science behind the itch
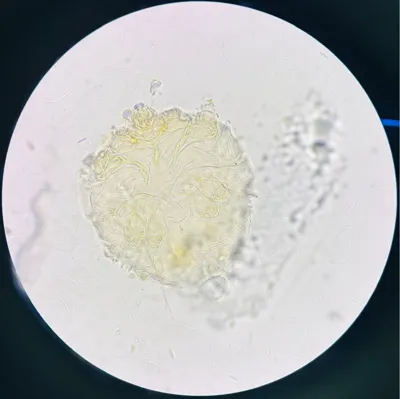
Microscopic view of Sarcoptes scabiei
The adult mites mate over the surface of the skin, fertilised female mite borrows into the outer layer of skin and start laying 2-3 eggs daily. It continues to burrow skin, forming tunnels even at a rate of 5mm a day. Larvae coming out of the eggs mature into adults, move on to the skin surface, mate and then the life cycle continues.
After 4-6 weeks of parasitic infestation, the affected person develops severe itching and a rash caused by an allergic reaction triggered by the presence of parasitic proteins and faeces. Because the source of the itch is a hypersensitivity reaction, it may persist for 2-4 weeks, even after treatments. Also, the itch tends to be more severe during the treatment.
How to identify scabies rash?
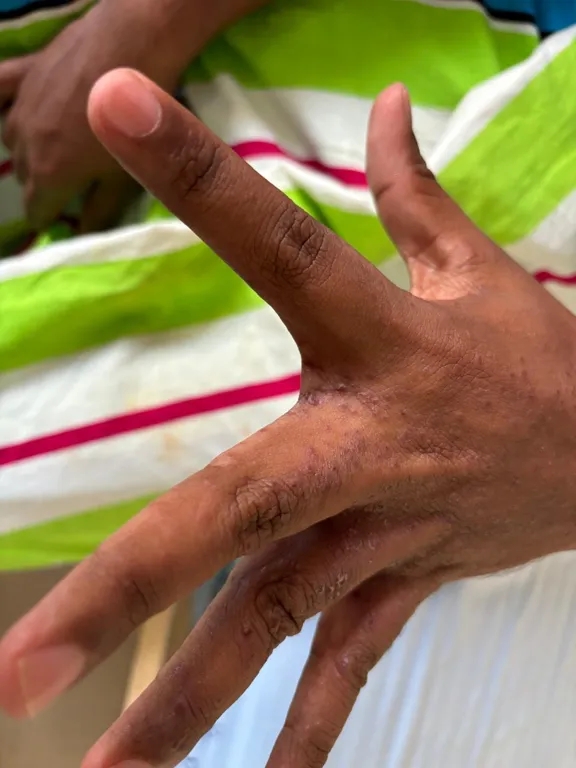
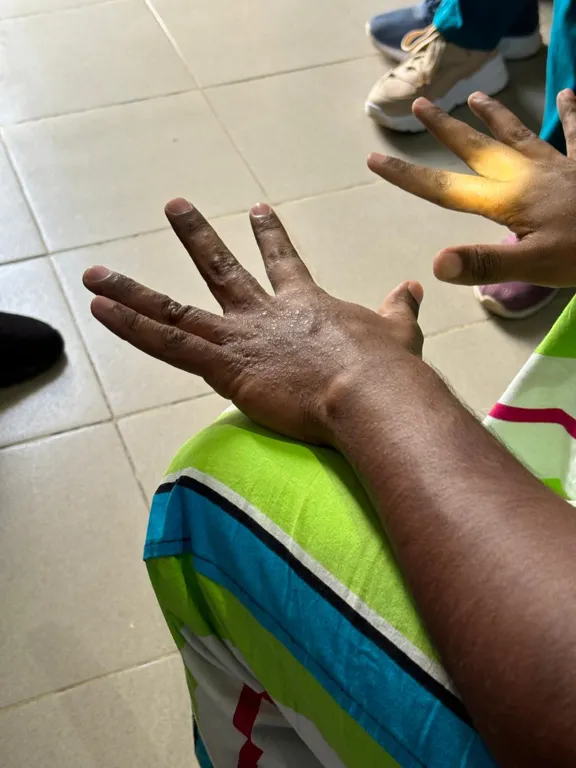
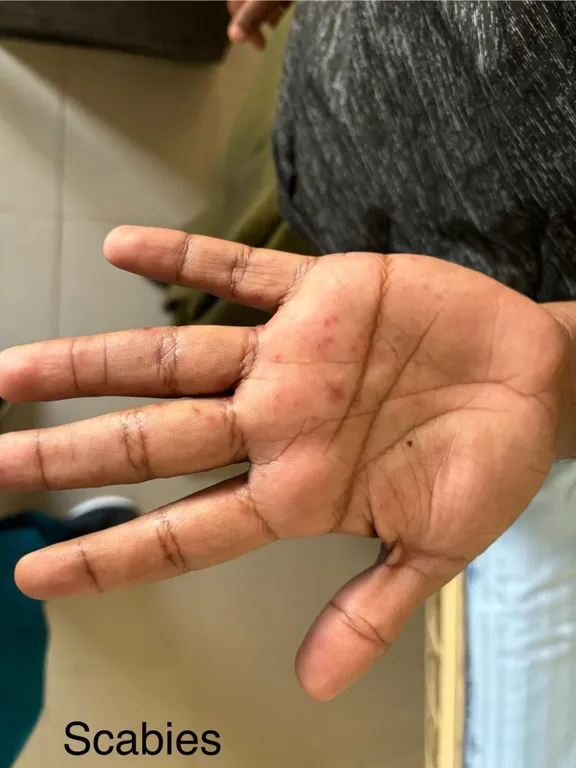
This typically presents with a characteristic itchy rash. Lesions are symmetrical and usually affect the hands, wrists, armpits, thighs, buttocks, feet, penis and scrotum of males, as well as the breasts and vulva of females. The head and neck are usually spared, except in babies, older people, and immunocompromised individuals.
Itch
- Widespread. Not limited to a specific body part
- Tend to worse at night
- Start 4-6 weeks following initial infection
- Occurs within hours in individuals previously has been infected
- Intensity may vary according to the individual (extreme itching up to mild manifestation)
- May persist several weeks even after completion of treatments
Rash
- Present at specific sites like hands, wrists, armpits, etc
- Reddish, tiny bumps
- May present with linear scratch marks
- Crusting (present dried serum, pus-like fluid over the lesion)
- Red-brown or skin color nodules
- Tiny blisters if there's a secondary bacterial infection
Burrows
- Curve and linear, thread-like pathways
- About 5-10 mm
- Present at typical sites like web spaces in between fingers, palms, soles, etc
Crusted scabies
- A rare type of scabies
- Palms and soles covers with crusted plaques
- Present in immunodeficient people (HIV), patients with leprosy
- Itch is less or even absent
- Present with thousands or even millions of mites
- Highly infectious
Scabies incognito
- The typical picture of scabies has been changed here due to inappropriate steroid application
How do you get scabies?
As described previously, it is transmitted through direct skin contact from human to human. Children contract it through close contact during play, leading to outbreaks in developed countries. Adults may acquire it via sexual contact.
Risk factors include:
- Crowded conditions
- Poverty
- Poor hygiene
- Malnutrition
- Homelessness
Like conditions lead to higher prevalence in low-income tropical countries.
However, it's impossible to spread the condition via fomites (towels, bed linen) because the parasitic mites usually die when they get out of the human body. In addition to a brief handshake, a hug is unlikely to spread the disease unless it is crusted scabies.
So, if you are not infected, avoid direct contact with affected people.
If you are already infected
- Cut your fingernails short
- Wash your towels and recently used garments in hot water and dry them under direct sunlight
- If washing is impossible, keep infected materials in a plastic bag for 7 days to ensure elimination of parasites
- Identify your close contacts and refer them for medical treatments, even if they are asymptomatic. This should be applied especially in households.
- Get medical treatments and follow the advice given
- Ensure that you are not transmitting the disease to anyone else!
Treatment methods
When you seek medical care, if it is confirmed as scabies, you would be prescribed topical applications or oral pills according to the severity.
- 5% permethrin cream or lotion is the first-line therapy.
Other available topical treatments are:
- 10–25% benzyl benzoate emulsion
- 0.5% malathion in aqueous base
- 5–10% sulphur ointment
It's essential to know the way of application. Apply the given application throughout the body below the jawline. It should be applied under nails, as well as between fingers. The application should be kept overnight for 8-12 hours. You should apply it again if you washed your hands during the treatment period. Infants, older people, and individuals with immunodeficiencies should apply it over the face and scalp. Topical applications do not kill parasitic eggs. So, the treatment should be repeated in 7-10 days.
Oral ivermectin is indicated in people with failed treatment with topical applications, in outbreaks, as well as mass drug administration (giving treatment to an entire population in an affected area). This process also should be repeated in 2 weeks. This is found to be highly effective; however, it is not recommended for pregnant mothers and children weighing less than 15 kg.
Scabies is a highly contagious parasitic disease that is treatable. It can lead to repeated infections, resulting in a significant psychological impact. Effective treatment methods available while adhering to the treatment is essential. Simultaneous treatment of close contacts should be done to prevent further disease transmission. Complete eradication of the parasite is a must. Mass drug administration in affected areas is practised by several countries already. It helps to reduce the cost of treatments and maintain societal productivity.



